Nanox
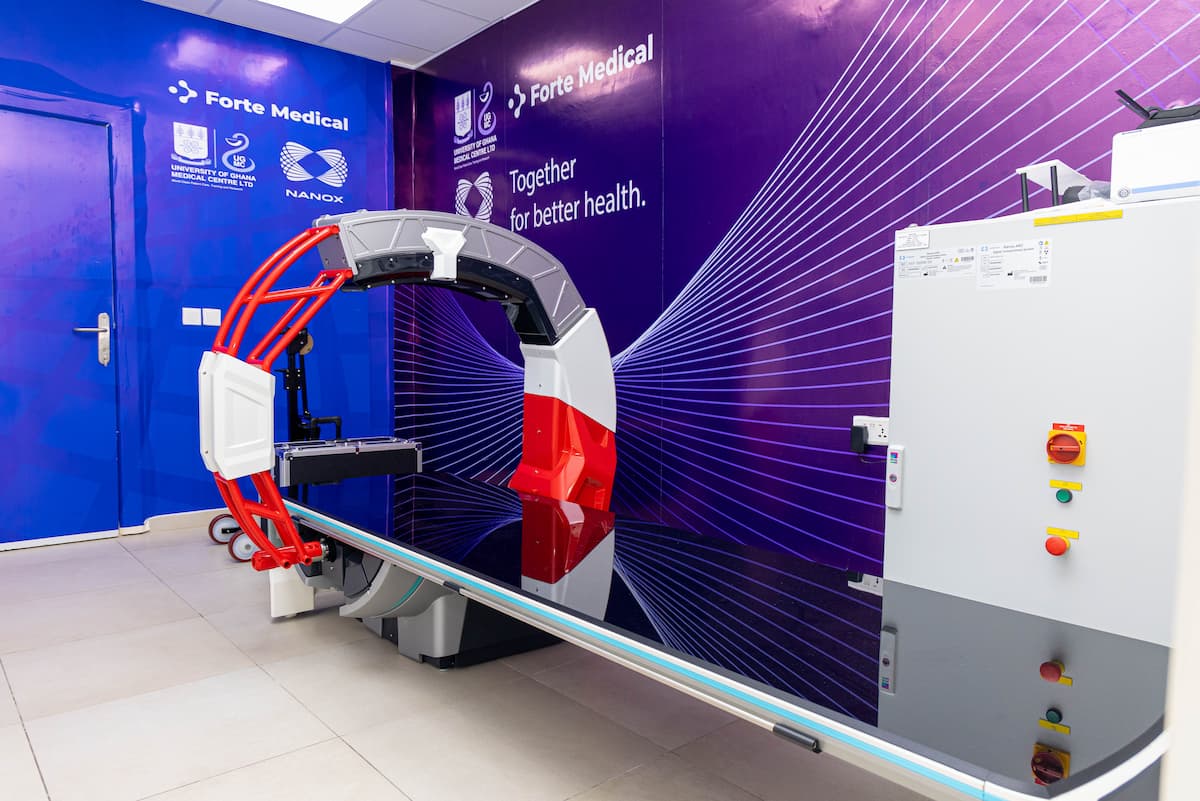
BackThe Radiology Department of the University of Ghana Medical Centre (UGMC) provides modern imaging services with the Nanox Arc system. Nanox imaging is a digital X-ray-based technique that produces high-quality diagnostic images while facilitating patient workflow. The technology is primarily used for general radiography examinations but may also give 3D tomosynthesis-like images for better anatomical visualisation when therapeutically necessary.
PATIENT PREPARATION
Patient preparation for Nanox imaging is generally minimal and similar to standard X-ray examinations. However, preparation depends on the body part being examined:
Patient preparation for Nanox imaging is generally minimal and similar to standard X-ray examinations. However, preparation depends on the body part being examined:
General preparation:
- Patients are required to present a valid imaging request form and any relevant previous imaging results.
- Metallic objects such as jewellery, belts, buttons, or coins should be removed from the area of interest, as these may interfere with image quality.
- Patients should inform the radiographer if there is any possibility of pregnancy, especially for examinations involving the abdomen or pelvis.
Specific preparation (where applicable):
- For chest and musculoskeletal examinations, no special preparation is usually required.
- For abdominal or pelvic imaging, patients may be advised on fasting or bladder preparation depending on the clinical indication.
SPECIFIC TIME SLOTS
Nanox imaging services are available during routine Radiology Department working hours at UGMC.
Nanox imaging services are available during routine Radiology Department working hours at UGMC.
- Examinations are performed by appointment for outpatients.
- Emergency and inpatient cases are accommodated based on clinical urgency.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE NANOX MODALITY
The Nanox Arc is an innovative digital X‑ray imaging system that uses multiple low‑energy X‑ray sources arranged in an arc configuration. Unlike conventional single‑source X‑ray systems, the Nanox Arc can acquire images from multiple angles around the patient.
The Nanox Arc is an innovative digital X‑ray imaging system that uses multiple low‑energy X‑ray sources arranged in an arc configuration. Unlike conventional single‑source X‑ray systems, the Nanox Arc can acquire images from multiple angles around the patient.
This technology enables:
- High-quality two-dimensional (2D) digital radiographs.
- Enhanced depth information through 3D tomosynthesis-like reconstruction (coronal slices), which can improve lesion detection and anatomical assessment.
- Efficient image acquisition with optimized radiation dose management.